areola
The areola is a pigmented area around the nipple that contains Montgomery glands and helps a baby find the breast.
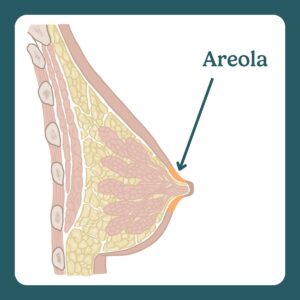
The areola is a pigmented area around the nipple that contains Montgomery glands and helps a baby find the breast.
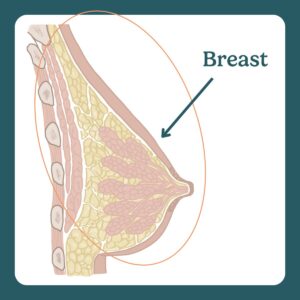
The breast is a glandular organ on the chest with lobules that produce milk and ducts that transport it.
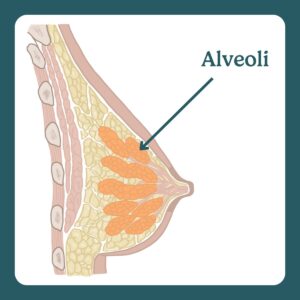
Alveoli are grape-like clusters in the breast that produce and store milk.
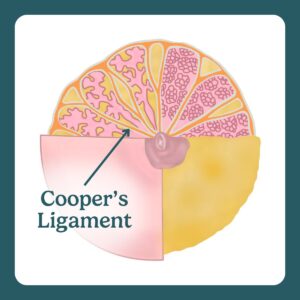
Cooper’s ligament is a connective tissue that supports and maintains the shape of your breasts.
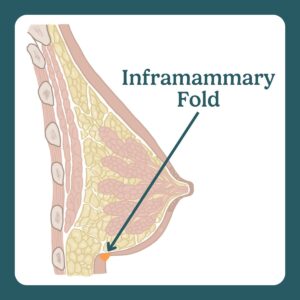
The inframammary fold is where the lower breast meets the chest wall.
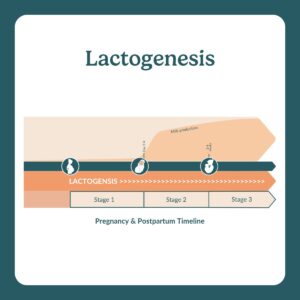
Lactogenesis is the three-stage process of milk production in the breast.

The let-down reflex is a process that releases milk during breastfeeding.

Lobes are sections in the breast containing clusters of milk-producing alveoli.
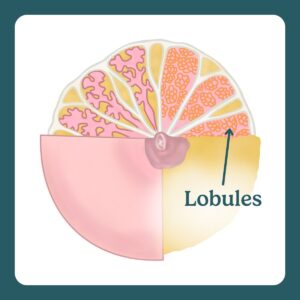
Lobules are small clusters in the breast containing milk-producing alveoli.
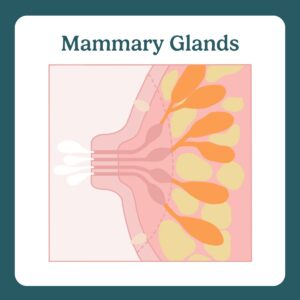
Mammary glands include alveoli and ducts that work together to produce and release milk.
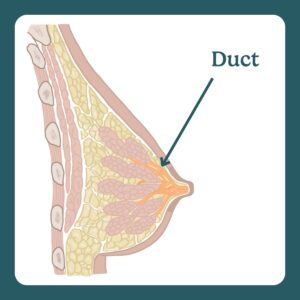
Milk ducts are tiny tubes in the breast that transport milk from alveoli to the nipple.
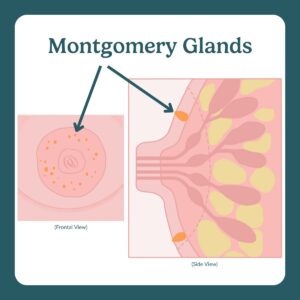
Montgomery glands are around the areola and help lubricate and guide the baby to the nipple.
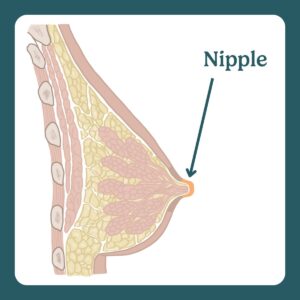
The nipple is the small, raised part of the breast where milk flows to your baby.
Oxytocin is a hormone known as the “love hormone” that helps trigger the let-down reflex during breastfeeding.
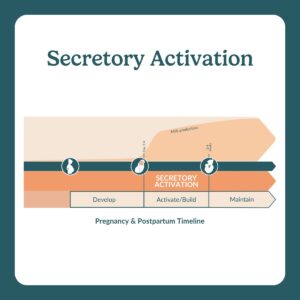
Secretory activation, or lactogenesis II, starts 2-4 days after birth, transforming colostrum to mature milk.
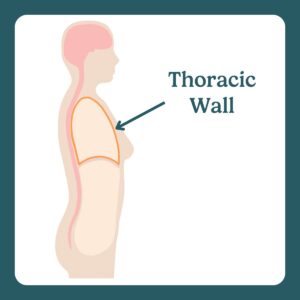
The thoracic wall consists of bones, muscles, and tissues that support the breasts.
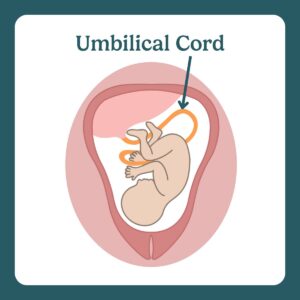
The umbilical cord connects the baby to the placenta and provides nutrients and oxygen.
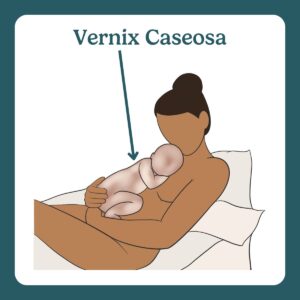
Vernix caseosa is a white, cheesy substance that protects and moisturizes a baby’s skin in the womb.