carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the main nutrients your body needs for energy. They are found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
During breastfeeding, carbohydrates are important because they provide energy for you and your baby and are a key component of your baby’s growth and development.
What to watch out for
Make sure you get enough carbohydrates while breastfeeding to maintain your energy levels and support your baby’s needs:
- Energy levels: Carbohydrates are your body’s main source of energy. Consuming an adequate amount of healthy carbs can help maintain your energy levels, which is crucial when caring for a newborn.
- Milk production: A balanced diet rich in carbohydrates can support adequate milk production. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy.
- Blood sugar regulation: Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, over simple sugars. Complex carbs help regulate blood sugar levels, providing steady energy and preventing spikes and crashes.
- Nutrient density: Choose nutrient-dense carbohydrate sources that also provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Examples include oats, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and berries. These foods support both your health and your baby’s development.
If you have concerns about your diet or energy levels, consult a healthcare provider or nutritionist for personalized advice.
Physical limitations or health circumstances
Certain conditions can affect how you utilize carbohydrates:
- Diabetes: If you have diabetes, managing carbohydrate intake is crucial to maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Work with a healthcare provider to create a balanced meal plan that supports both your health and breastfeeding. Learn more about breastfeeding with diabetes.
- Celiac disease: Individuals with celiac disease need to avoid gluten, a protein found in certain grains. Choose gluten-free carbohydrate sources such as rice, quinoa, and gluten-free oats to ensure adequate carbohydrate intake.
- Lactose intolerance: If you are lactose intolerant, opt for lactose-free dairy products or alternative sources of carbohydrates such as plant-based milk, fruits, and vegetables.
Other terms
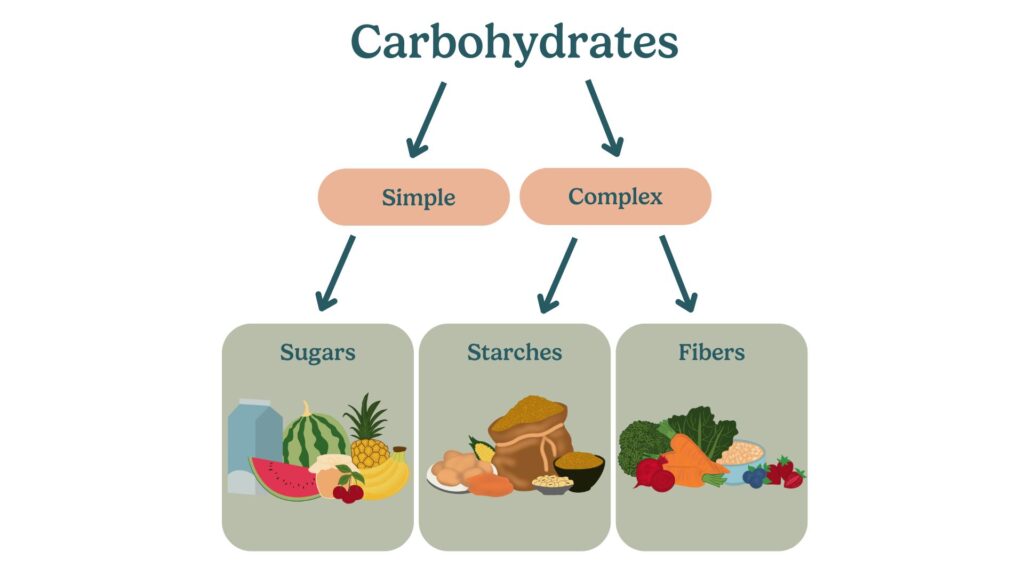
- Complex carbohydrates: Carbohydrates that are made up of long chains of sugar molecules. They provide sustained energy and are found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Simple carbohydrates: Carbohydrates that are made up of one or two sugar molecules. They provide quick energy but can lead to blood sugar spikes. Found in foods like sugary snacks, sodas, and refined grains.
- Fiber: A type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It helps regulate the body’s use of sugars, keeping hunger and blood sugar in check. Found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Glycemic index (GI): A measure of how quickly a food causes blood sugar levels to rise. Foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and legumes, provide more stable energy levels.
- Starch: A type of complex carbohydrate found in foods like potatoes, rice, and corn. Starches provide a good source of energy for both you and your baby.